GraphQL & Apollo
GraphQL
- GraphQL은 SQL와 같은 Query언어이다.
- GraphQL은 하나의 형식, 즉 명세이기 때문에 이를 구현할 방법이 필요한데 그 중 하나가 Apollo이다.
Apollo
- Apollo는 GraphQL을 편하게 사용할 수 있도록 도와주는 라이브러리이다.
- Apollo는 client와 server에서 모두 사용가능하다.
- Apollo Server를 이용해 GraphQL이 적용된 백엔드 서버를 제작할 수 있고,
- Apollo Client를 활용하여 client상의 localstate를 이용할 수 있다.
Setup
npm install @apollo/client graphql- @apollo/client: This single package contains virtually everything you need to set up Apollo Client. It includes the in-memory cache, local state management, error handling, and a React-based view layer.
- graphql: This package provides logic for parsing GraphQL queries.
graphQL
- rest API는 overfetching과 여러개의 url에서 로딩이 필요하다는 단점이 있다.
- 이러한 rest API의 문제점을 graphql API가 해결한다.
( While typical REST APIs require loading from multiple URLs,
GraphQL APIs get all the data your app needs in a single request.)
[GraphQL의 장점]
1. 필요한 정보들만 선택하여 받아올 수 있다.
- Overfetching 문제 해결
- 데이터 전송량 감소 (빨라짐)
2. 여러 계층의 정보들을 한 번에 받아올 수 있다.
- Underfetching 문제 해결 (API request가 필요한 data를 다 주지않는 문제)
- 데이터 요청 횟수 감소
3. 하나의 endpoint에서 모든 요청을 처리한다.
- 하나의 URI에서 POST로 모든 요청 가능 ( query, mutation등의 명령어로 get, post를 요청 )
[특징]
rest api는 많은 url들을 집합인 반면, graphQL은 많은 type들의 집합이라고 할 수 있다.
type을 만드는것은 rest API의 GET request를 만드는 것과 같다.
//rest api
GET /api/v1/tweet/:id
//graphQL
type Query {
tweet(id: ID) : Tweet
}
Apollo
✔️ GraphQL Playground
: 작성한 GraphQL type, resolver 명세 확인
데이터 요청 및 전송 테스트
graphql Query language
✔️ Apollo server구축
const { ApolloServer, gql } from 'apollo-server';
//GraphQL에서 사용될 데이터, 요청의 타입 지정
//gql(template literal tag)로 생성됨
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
teams: [Team]
}
type Team {
id: Int
manager: String
office: String
extension_number: String
mascot: String
cleaning_duty: String
project: String
}
`;
// 서비스의 action들을 함수로 지정
// 요청에 따라 데이터를 반환, 입력, 수정, 삭제
const resolvers = {
Query: {
teams: () => database.teams,
},
};
//ApolloServer : typeDef와 resolver를 인자로 받아서 서버를 생성
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
server.listen().then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at ${url}`);
});
📌 코드 설명
- graphql SDL (graphql schema definition language)
: typeDefs에 Query라는 root type을 작성해야한다.
- Query root type
: user의 request에 의해 사용될 query들을 정의하는 가장 기본적이고 필수인 type.
: rest API에서 GET url을 만드는거랑 동일.
//GET /text와 동일한 의미
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
text : String
}
`;
//temas query를 날리면 여러개의 Team 데이터가 날라온다. (배열)
type Query {
teams: [Team]
}
- Type
: 반환될 데이터의 형태를 지정
자료형을 가진 필드로 구성
type Team {
id: Int
manager: String
office: String
extension_number: String
mascot: String
cleaning_duty: String
project: String
}
- Resolver
: Query란 object의 항목들로 데이터를 반환하는 함수를 선언.
(database의 teams를 반환하는 함수)
const resolvers = {
Query: {
teams: () => database.teams
}
}
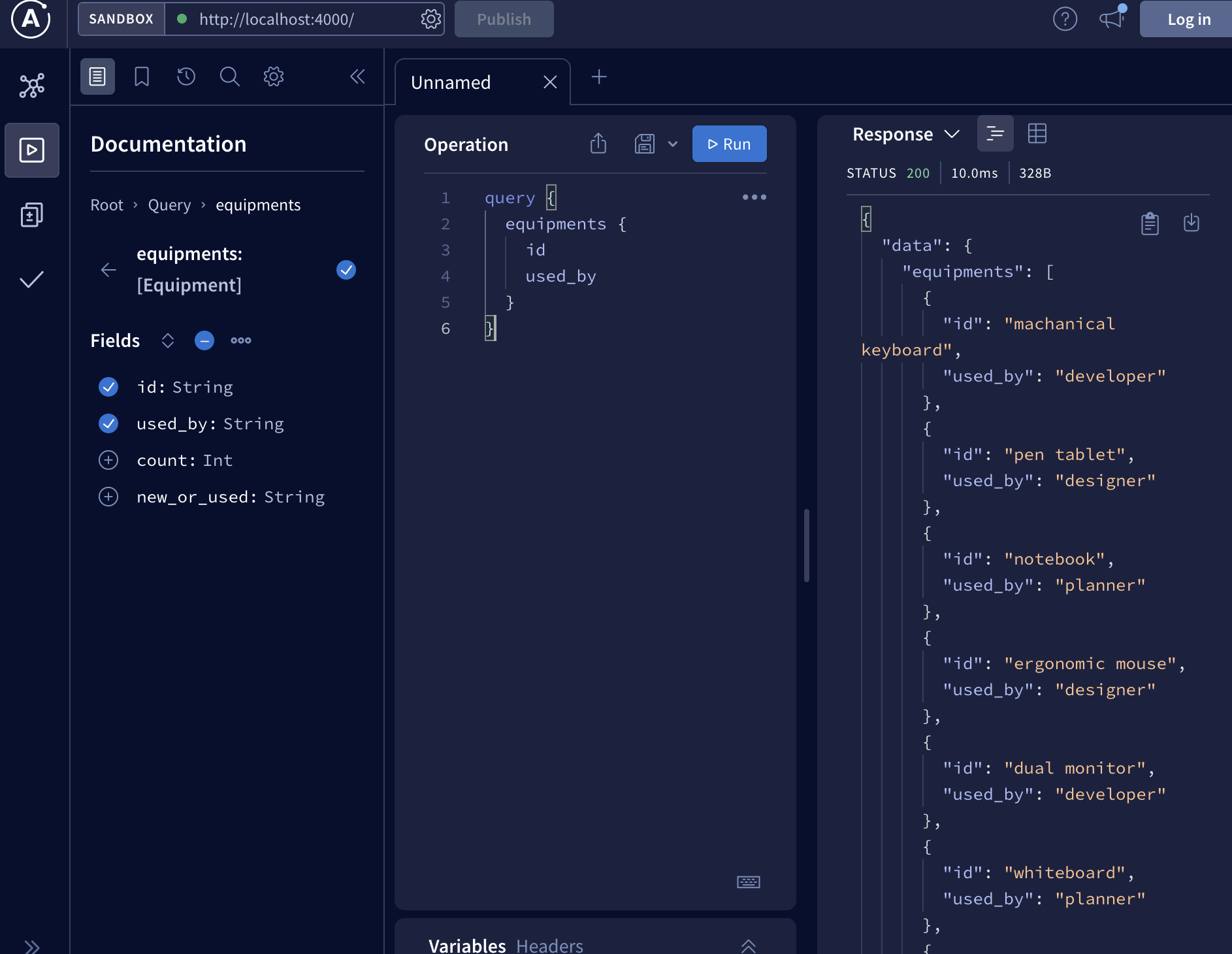
➡️ query 만들어보기 예제
equipments.csv
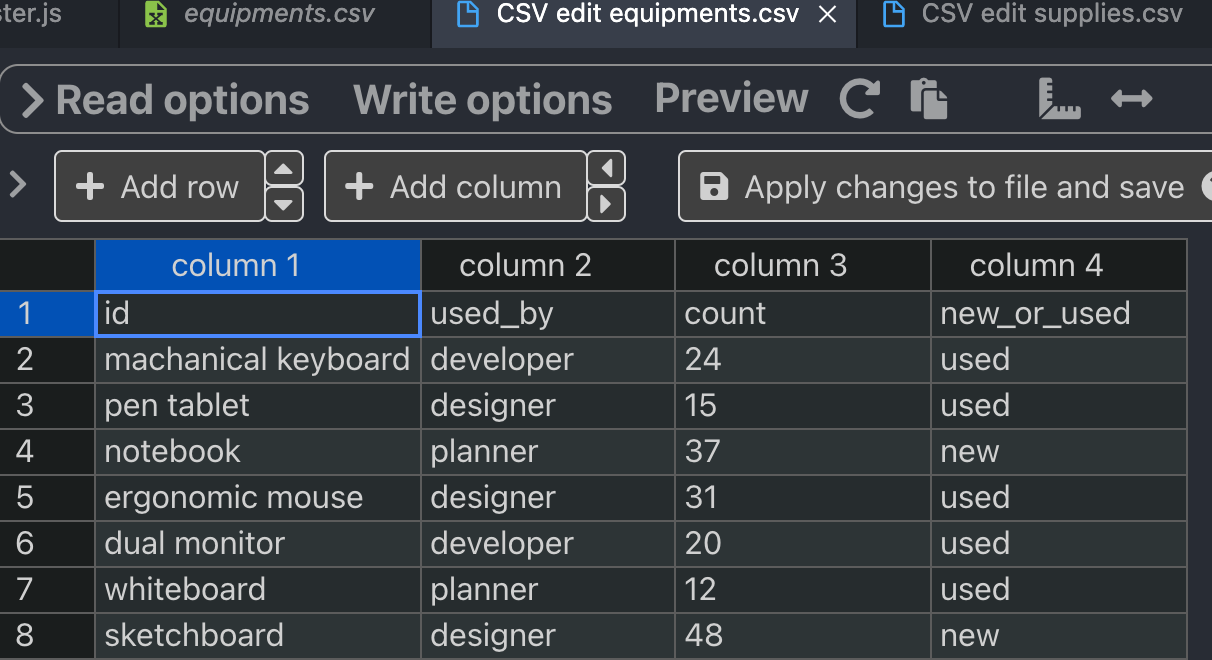
//dbtester.js
const database = require('./database');
console.log(database.equipments);const database = require('./database');
const { ApolloServer, gql } = require('apollo-server');
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
equipments: [Equipment]
}
type Equipment {
id: String
used_by: String
count: Int
new_or_used: String
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Query: {
equipments: () => database.equipments,
},
};
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });
server.listen().then(({ url }) => {
console.log(`🚀 Server ready at ${url}`);
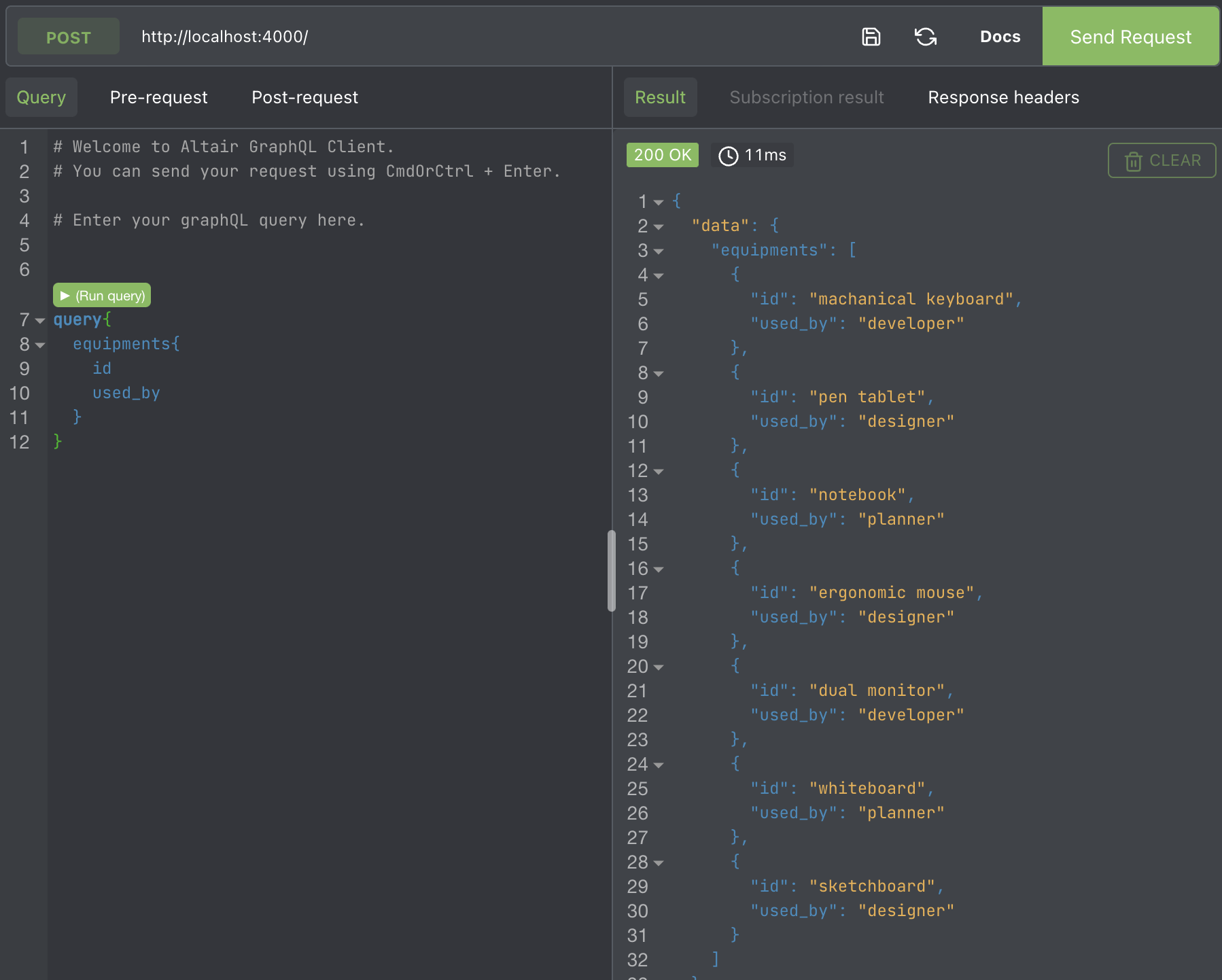
});npm start
http://localhost:4000 으로 query요청
//query 요청
query {
equipments {
id
used_by
count
new_or_used
}
}
➡️ 특정 데이터만 받아오기 예제 ( argument )
args로 주어진 id에 해당하는 team만 필터링하여 반환([0]첫번째 데이터만 받아오기)
Query: {
team: (parent, args, context, info) => database.teams
.filter((team) => {
return team.id === args.id
})[0],
}GET /api/team/:id 와 동일
type Query {
...
team(id: Int): Team
}id:1번의 데이터만 받아오기
{
team(id: 1) {
id
manager
office
}
}
Mutation
🔻 데이터를 삭제, 추가, 수정 시 Mutation을 사용한다.
POST / DELETE / PUT의 기능
type Mutation {
변경데이터이름(id: String): 반환값
}
server에서 type Mutation 지정
const typeDefs = gql`
type Tweet {
id : ID
text : String
}
type Query {
Tweet (id:ID) : Tweet
}
type Mutation {
postTweet(text:String, userId : ID) : Tweet
}
`;mutation {
postTweet(text:"Hello", userId:"1"){
text
}
}
[삭제]
root type
// String 인자 id를 받는 delete~ : 삭제된 Equipment를 반환한다.
type Mutation {
deleteEquipment(id: String): Equipment
}
// 혹은 boolean으로 삭제되면 true아니면 false
type Mutation {
deleteEquipment(id: String): Boolean
}//resolver
Mutation: {
deleteEquipment: (parent, args, context, info) => {
const deleted = database.equipments
.filter((equipment) => {
return equipment.id === args.id
})[0]
database.equipments = database.equipments
.filter((equipment) => {
return equipment.id !== args.id
})
return deleted
}
}//playground
mutation {
deleteEquipment(id: "notebook") {
id
used_by
count
new_or_used
}
}
Nullable Fields
특별히 지정해주지 않는다면 query는 기본적으로 nullable fields를 가진다.
(해당값 혹은 null이 될 수 있다는 의미)
type User {
id: ID
email: String
// email : String | null
}
null값을 허락하고 싶지않다면, 값을 필수로 만들고 싶다면(required) "!" 를 적어준다.
!로 지정해준 값에 null이 나오면 error가 발생한다.
// postTweet 하려면 text를 무조건 보내야하고 그것은 무조건 String이어야한다!
// 그러면 항상 Tweet가 반환될것이야!!!
type Mutation {
postTweet(text: String!): Tweet!
}
배열이 비어있으면 error가 발생하지 않는다.
? 비어있는 것은 null이 아니기 때문
// allTeam은 항상 list가 되어야하고, 그 list는 항상 Team이다.
type Query {
allTeam : [Team!]!
}
Resolvers
- schema field에서 사용되는 (Query, Mutation)함수의 실제행동을 Resolvers에서 정의한다. (Query실제로 일을 하는 부분 )
- Resolver 함수에는 parent(root source), args, context, info의 네 가지 인자가 순서대로 전달된다.
import { ApolloServer, gql } from 'apollo-server';
const typeDefs = gql`
type Query {
ping: String!
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Query: {
ping() {
return 'pong';
},
},
};
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });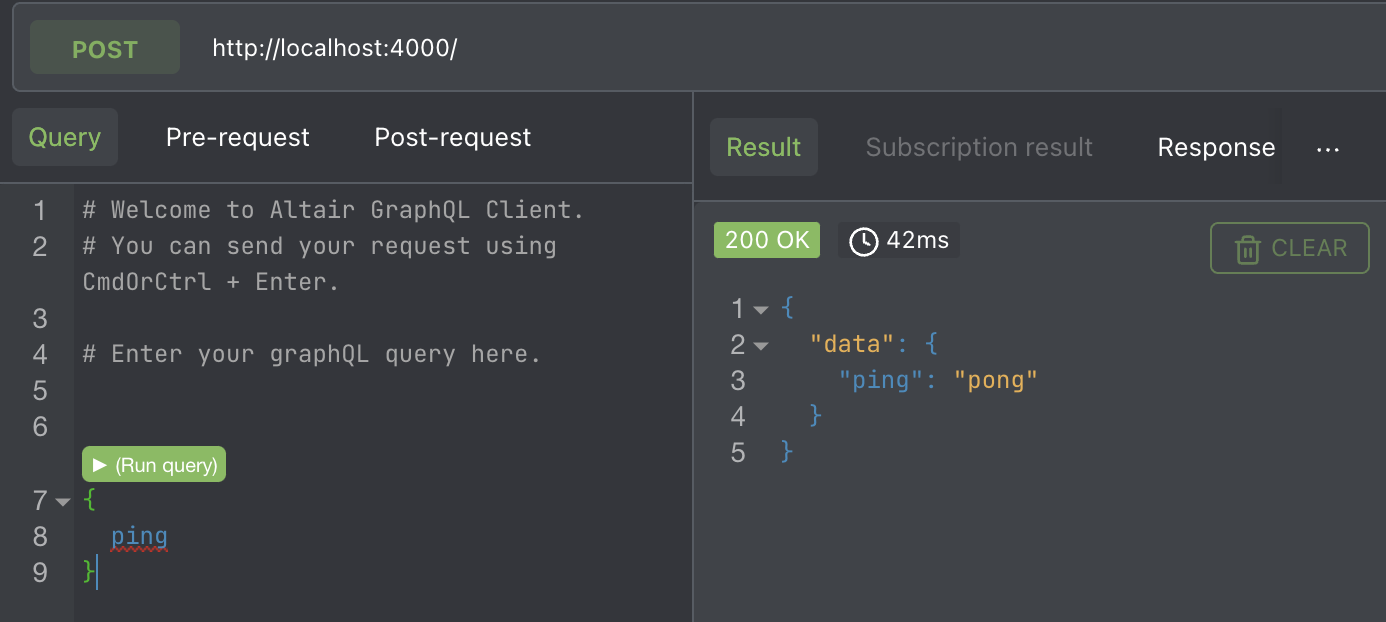
Arguments
- user가 arguments를 보내면 그 args는 항상 resolvers의 두번째 인자로 들어온다.
let tweets = [
{
id: '1',
text: 'first',
},
{ id: '2',
text: 'second'
},
];
const typeDefs = gql`
type Tweet {
id: ID!
text: String!
author: User
}
type Query {
tweet(id: ID!): Tweet
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Query: {
tweet(_, { id }) {
return tweets.find((tweet) => tweet.id === id);
},
},
};
const server = new ApolloServer({ typeDefs, resolvers });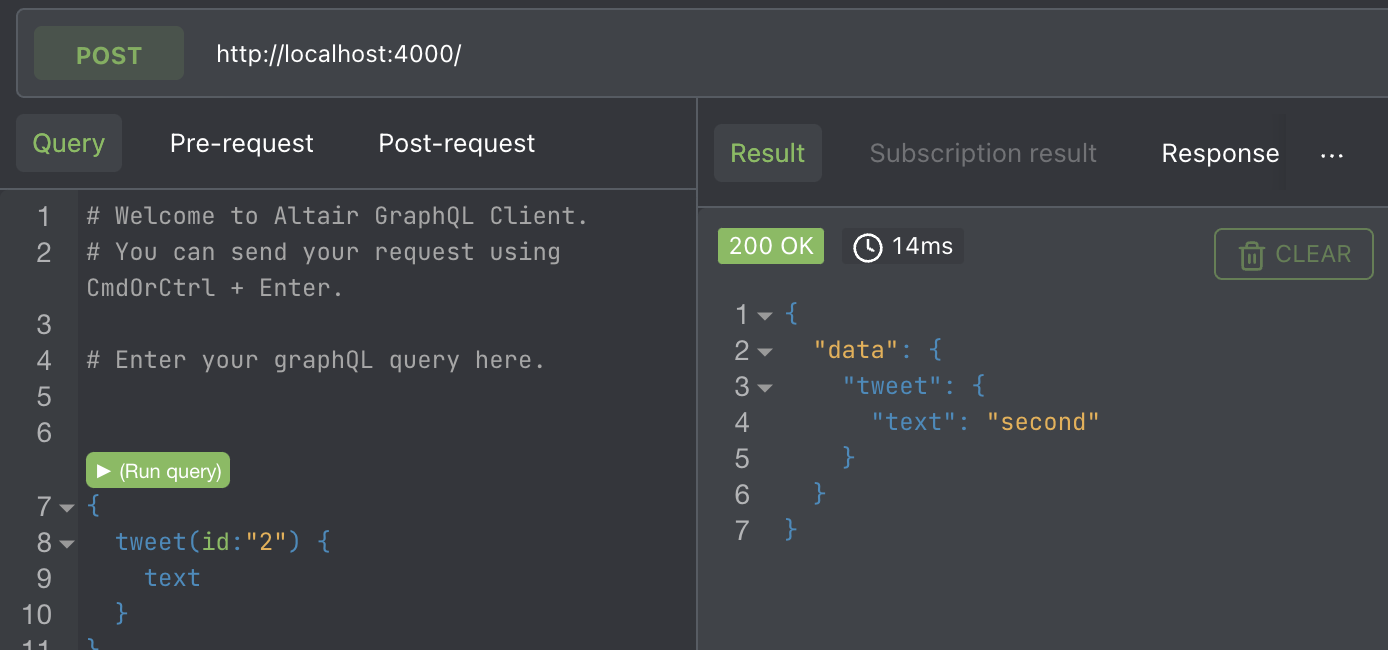
✔️ Mutation의 resolvers 예시
const typeDefs = gql`
type Mutation {
postTweet(text: String!, userId: ID!): Tweet
deleteTweet(id: ID!): Tweet
}
`;
const resolvers = {
Mutation: {
postTweet(_, { text, userId }) {
const newTweet = {
id: tweets.length + 1,
text,
};
tweets.push(newTweet);
return newTweet;
},
deleteTweet(_, { id }) {
const deleteTweet = tweets.find((tweet) => tweet.id === id);
if (!deleteTweet) return false;
tweets.filter((tweet) => tweet.id !== id);
},
},
};
Root
- Resolvers의 첫번째 인자로 항상 root code가 전달된다.
let users = [
{
id: '1',
firstName: 'manon',
lastName: 'kim',
},
{
id: '2',
firstName: 'manon2',
lastName: 'kim2',
},
];const typeDefs = gql`
type User {
id: ID!
firstName: String!
lastName: String!
fullName: String!
}
type Query {
allUsers: [User!]!
}
`;
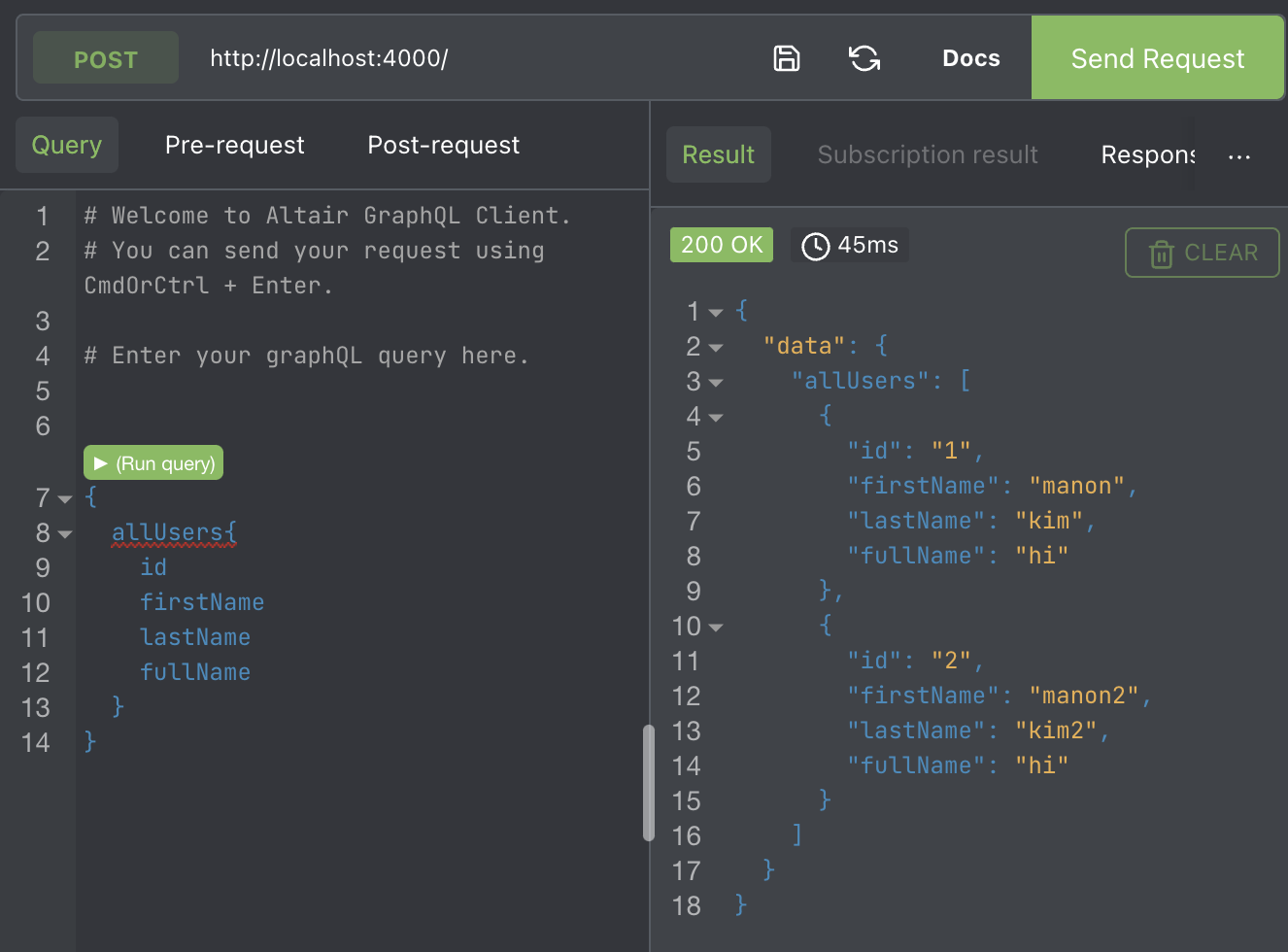
const resolvers = {
Query: {
allUsers(root) {
console.log('allUsers called');
console.log(root);
return users;
},
},
User: {
fullName(root) {
console.log('fullName called');
console.log(root);
return 'hi';
},
},
};
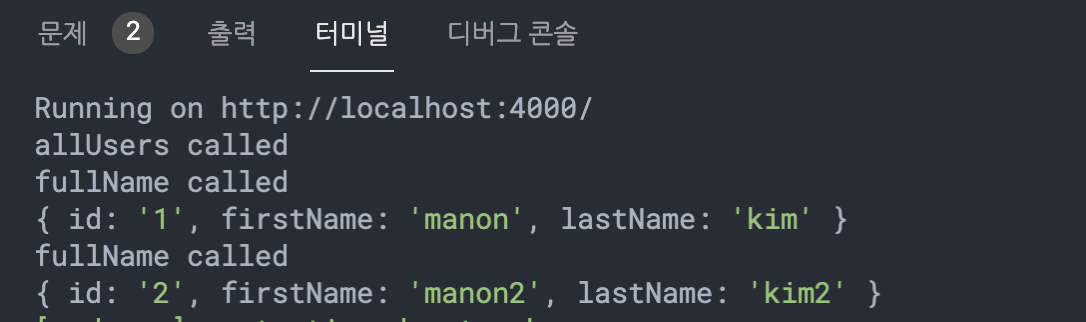
allUsers를 호출
1. resolvers의 Query - allUsers가 제일먼저 호출 (console에 'allUsers callled')
2. 호출해야하나느 user가 2개가 있어서 graphql은 User를 두번 찾는다. (consoledp 'fullname called'가 두번찍힘)
첫번째 호출될 때는 id:1의 root - 두번째 호출 될 때는 id L:2의 root가 호출
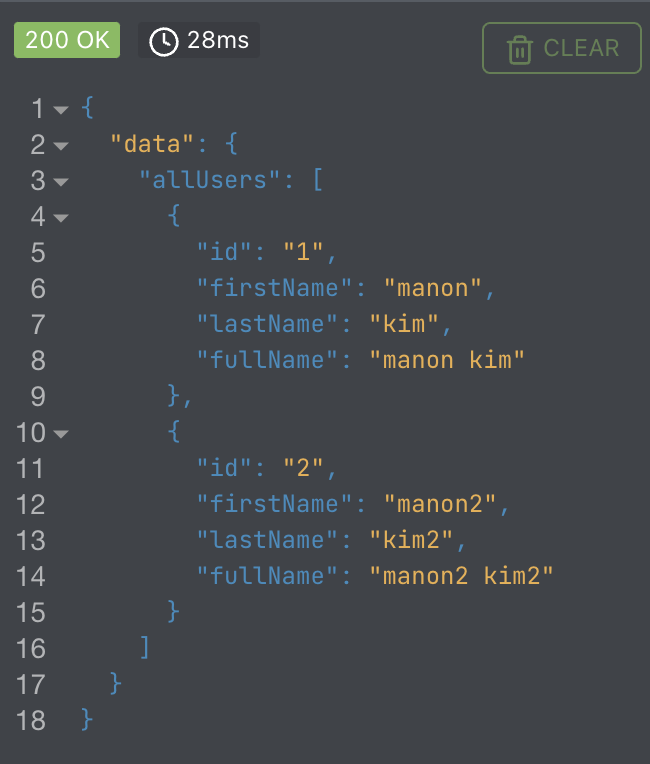
root를 활용
const resolvers = {
User: {
fullName({firstName, lastName}) {
return `${firstName} ${lastName}`;
}
}
Documentation
Altair같은 graphql client에서 type에 대한 설명을 Docs로 확인할 수 있다.
graphql은 서버에서 type 지정하는 부분에서 간단하게 documentation 기능을 사용할 수 있다.
const typeDefs = gql`
type Mutation {
postTweet(text: String!, userId: ID!): Tweet
"""
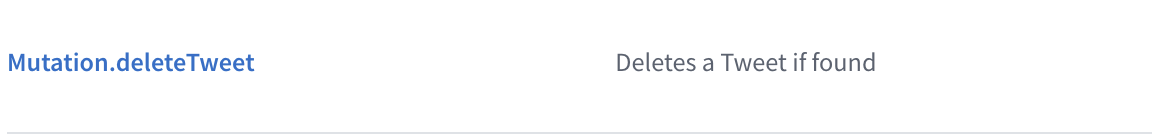
Deletes a Tweet if found
"""
deleteTweet(id: ID!): Tweet
}
`;
공식사이트
https://www.apollographql.com/
Apollo GraphQL | Supergraph: unify APIs, microservices, & databases in a composable graph
Apollo Graph Platform — unify APIs, microservices, & databases into a graph that you can query with GraphQL
www.apollographql.com
'Archive' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [React] React Hook Form (0) | 2022.05.08 |
|---|---|
| [TS] TypeScript Basic (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| [TIL220410] PlanetScale (serverless DB platform) (0) | 2022.04.10 |
| [TIL220407] Tailwind CSS (0) | 2022.04.07 |
| [Next.JS] NextJS 기초 (0) | 2022.04.02 |